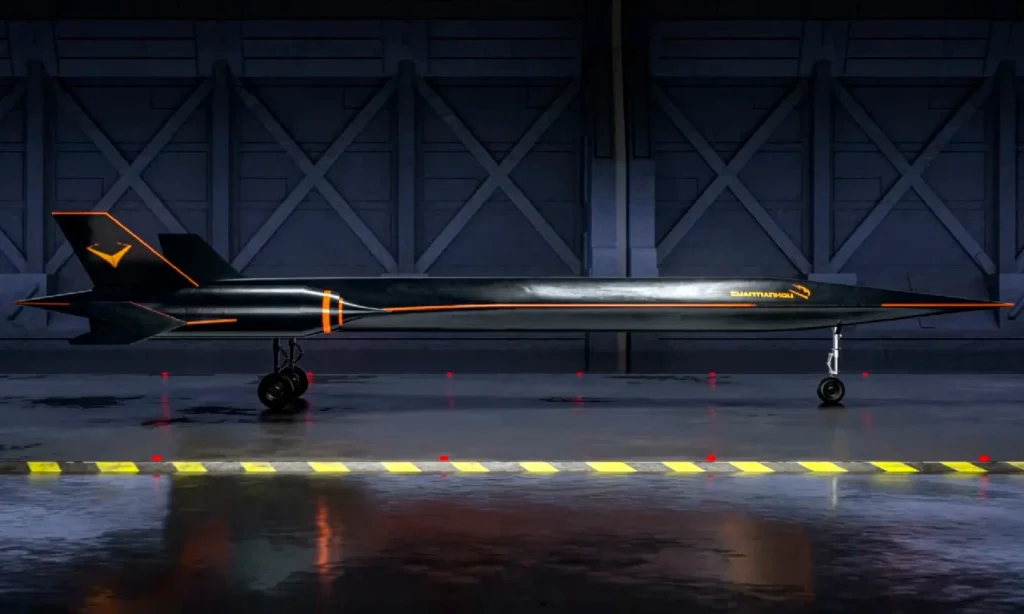
China recently revealed a groundbreaking supersonic jet prototype, making headlines globally with its promise to revolutionize air travel. Developed by a Chinese company named Space Transportation, or Lingkong Tianxing Technology, this high-speed jet is designed to travel at speeds reaching Mach 4, or four times the speed of sound. If successful, the jet could significantly shorten international flight durations, potentially enabling passengers to travel from Beijing to New York in just two hours. With plans to have a full-sized version ready for a maiden flight by 2027, China’s foray into supersonic aviation marks a major step in the competitive race toward next-generation air travel.
A Historic Milestone in Supersonic Aviation
The concept of supersonic commercial travel is not new. The Concorde, a joint effort by French and British aerospace companies, previously offered flights at twice the speed of sound starting in 1976. However, due to high operational costs, limited passenger capacity, and environmental concerns, the Concorde was retired in 2003. Since then, various aerospace companies have shown interest in reviving supersonic travel, but China’s recent developments with Space Transportation’s Yunxing prototype have given a new spark to the vision of ultra-fast travel.
This recent test flight of the Yunxing prototype marks a critical point in the journey. Achieving speeds that double those of the Concorde, Space Transportation’s aircraft aims to solve many of the challenges that grounded earlier supersonic endeavors. This includes advanced fuel efficiency, noise reduction for sonic booms, and improved thermal management to withstand the high temperatures generated at Mach 4 speeds.
Technical Highlights and Innovations
Space Transportation’s Yunxing prototype is designed not only for speed but also for stability, efficiency, and safety. Unlike the traditional jet engines, which limit commercial jets to subsonic speeds, the Yunxing prototype employs a new form of propulsion technology that allows it to achieve the high thrust necessary for supersonic speeds. A follow-up assessment of this engine technology is scheduled for November 2024, a step that will be crucial in determining the project’s viability.
The prototype utilizes cutting-edge aerodynamic designs and advanced materials capable of withstanding extreme temperatures at high speeds. Achieving Mach 4 requires engineering that balances thrust and heat dissipation while maintaining fuel efficiency. Materials with high thermal resistance are crucial to prevent overheating, especially at cruising speeds of around 5,000 kilometers per hour. Furthermore, innovative design choices help to minimize the noise associated with breaking the sound barrier—a critical factor for commercial operations that aim to reduce their environmental impact.
Another aspect under development is the management of the “sonic boom,” the loud noise produced when an object travels faster than the speed of sound. Space Transportation is exploring ways to reduce this impact, a concern that plagued the Concorde and caused frequent flight restrictions over populated areas. By focusing on advanced aerodynamic designs that minimize the noise, China aims to make supersonic travel more practical and widely acceptable.
Timeline and Future Prospects
Space Transportation envisions having a full-scale supersonic jet ready for its first flight in 2027. If achieved, this would mark a historic shift in long-distance air travel, making flights between continents a matter of hours. The jet’s anticipated capabilities are particularly striking: at Mach 4, passengers could travel from Beijing to New York in approximately two hours—a journey that currently takes over 13 hours on a conventional subsonic flight.
The development of this prototype also reflects China’s growing interest in commercial space exploration and high-speed transportation technology. With Space Transportation’s achievements, China demonstrates not only its potential to advance supersonic travel but also its aspirations to lead in a field that has traditionally been dominated by Western aerospace companies.
Challenges and Competition
While the Yunxing prototype shows immense promise, significant challenges remain. Fuel efficiency is one of the biggest concerns, as supersonic speeds generally demand more fuel, making it a costlier alternative to traditional commercial flights. Additionally, safety issues associated with high-speed flight must be addressed, especially in managing thermal effects and structural integrity under extreme conditions.
Moreover, China’s supersonic ambitions are not unfolding in isolation. Companies in the United States and Europe, such as Boom Supersonic and Aerion Corporation, have also been pursuing high-speed aviation, each vying to be the first to bring next-generation supersonic jets to commercial markets. Boom Supersonic, for example, is working on a jet named Overture, targeting a speed of Mach 1.7, while Aerion was developing the AS2, projected to reach Mach 1.4 before the company ceased operations in 2021 due to funding issues. These developments hint at a potential race, with China, the U.S., and other countries competing to be the leader in the revival of supersonic commercial travel.
Environmental and Regulatory Concerns
While technological advancements make supersonic travel feasible, environmental and regulatory challenges loom. Supersonic jets consume large amounts of fuel, leading to significant carbon emissions—a point of concern as countries aim for greener and more sustainable aviation solutions. Additionally, international aviation bodies have stringent regulations on noise pollution, and supersonic jets often face restrictions on routes over land due to sonic booms.
Space Transportation’s approach to minimizing sonic booms and improving fuel efficiency reflects an awareness of these issues. However, the full-scale adoption of supersonic jets will likely require new environmental guidelines and a commitment to sustainable practices. International cooperation may also be necessary, as supersonic jets would inevitably operate across multiple countries and continents.
A New Era in Aviation?
The potential for supersonic travel to reshape global connectivity is vast. The ability to reach destinations within a fraction of the time taken by current aircraft could open doors for business travel, tourism, and even diplomatic engagements, all while fostering stronger global ties. By investing in supersonic technology, China is making a statement about its ambitions in aerospace and commercial aviation. This project could place China at the forefront of a new era of transportation if the technical, regulatory, and environmental hurdles can be successfully navigated.
The Yunxing prototype and its planned successors could make the world feel smaller and more connected than ever before. Although there is still a long road ahead, China’s supersonic jet initiative represents a significant leap forward in realizing the dream of high-speed, efficient, and practical air travel.
“Stay In Touch With Us For More Latest News & Updates. Follow Us On Twitter and Facebook To Stay Aware”